A great start usually precedes great succes. When one of India’s biggest steel manufacturers required a heat exchanger solution, Kinam was able to meet their requirements with their first-ever K-SPEX Spiral Heat Exchanger. In this case study, we share how we were able to launch a new product that exceeded our client’s expectations.
The Clients Process:
Our clients operated a coke oven by-product plant. From coke oven, desirable hydrocarbons and other compounds like naphthene, benzene, and ammonia are recovered as a by-product by scrubbing using a scrubbing solution called lean oil.
These compounds are extracted by heating the rich solvent in a stripper and turning it into a lean solvent.
The solvent is cooled in 2 stages, first to approximately 45’C with cooling water, and then to 22’C with the use of chilled water.
The plant was supplied by a Chinese manufacturer. The solvent used is incredibly fouling in nature, which is why all Heat Exchangers used for cooling solvents were done using spiral heat exchangers.
The Issues:
Our client had an issue with the lifespan of the Chinese Heat Exchangers. Within 2-3 years of operation, these Spiral Heat Exchangers would begin to show signs of leakage. Even after replacement, these issues persisted.
As these exchanges were fully welded, making them difficult to clean and maintain. In addition to this, the MOC for these Heat Exchangers was Carbon Steel, which was not ideal for the application. Furthermore, the design of the Heat Exchanger was not ideal for the application.
As their current Heat Exchangers were coming to the end of their operating life, the steel manufacturing giant made the decision to replace all their Chinese Heat Exchangers with those of Indian make.
Kinam’s Solution:
During our initial discussions, we contemplated replacing the spiral heat exchangers with KICC Corrugated Heat Exchangers. However, due to the following reasons, Corrugated Tube Heat Exchangers were not applicable:
- Specific solutes get saturated and crystalize below 40C
- Space constraint: A Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger for the same load would be almost twice the size
- Increased size would increase material costs, making it more expensive for our clients
Moreover, the inherent fouling nature of the solvent made it more favourable to use Spiral Heat Exchanger technology.
It was during this time that Kinam also developed its K-SPEX Spiral Heat Exchangers. While we hadn’t supplied any spiral heat exchanger before, impressed by the amount of research we had done on the product, they were happy to accept our proposal.
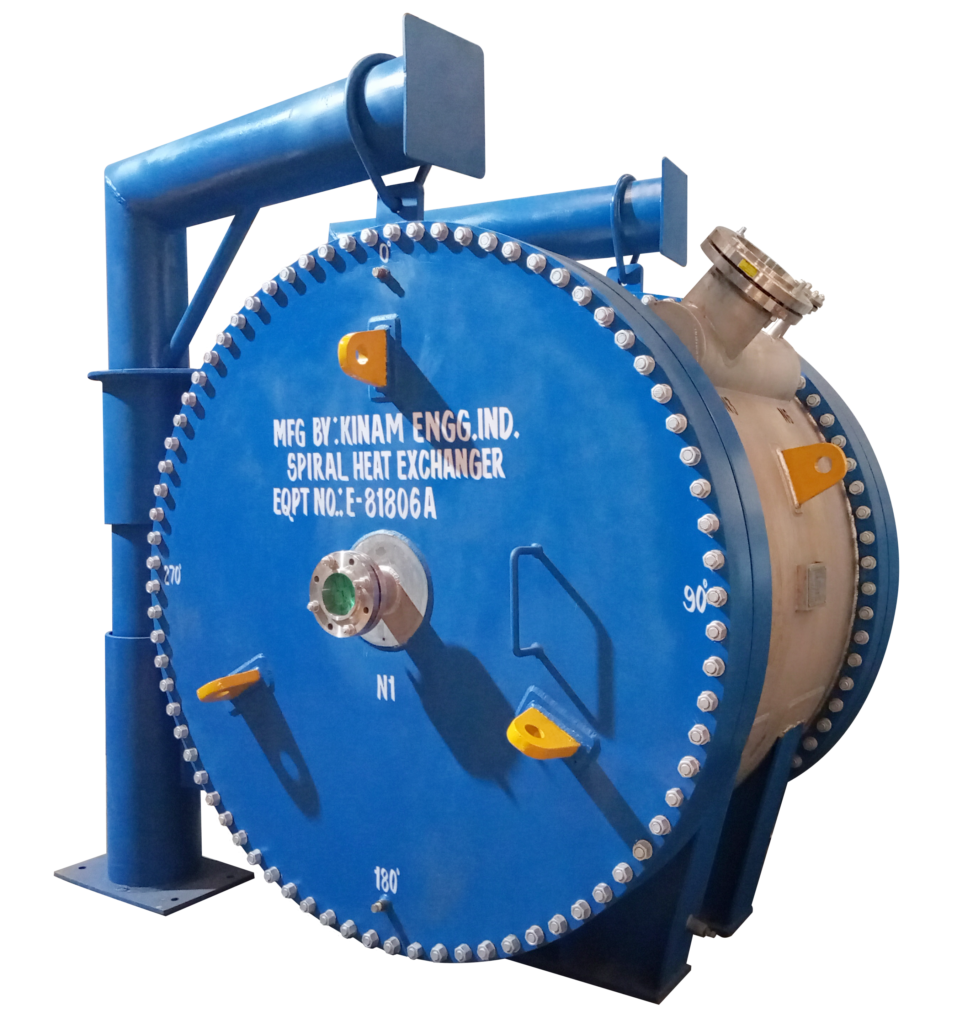
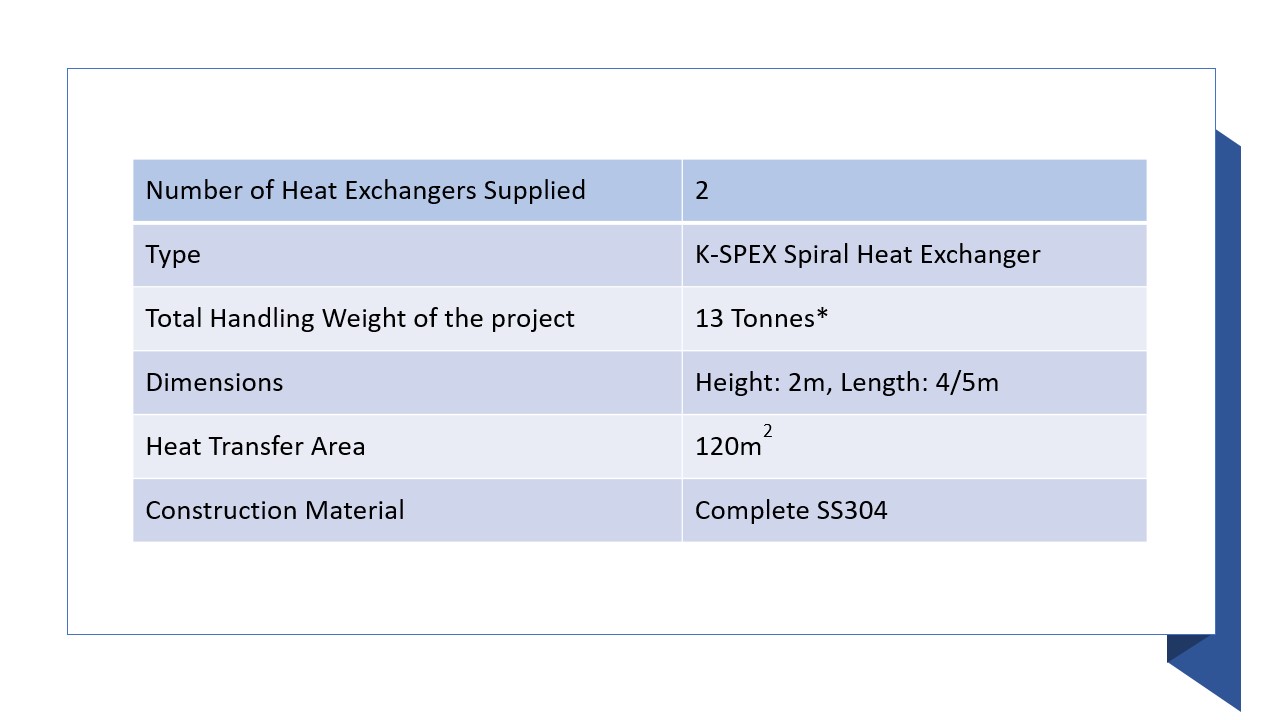
We supplied 2 Heat Exchangers of 120m2 heat transfer area, which would cost our clients a total of 1.2 Cr, beating one of the largest suppliers of Spiral Heat exchangers to the order. These K-SPEX Heat Exchangers were made of SS304 material and are both side openable.
Conclusion:
As mentioned earlier, spiral heat exchangers are more suited to be used with a fouling medium like the solvents. The K-SPEX was more economical and had a much smaller footprint than a Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger for the same application.
Since the K-SPEX is openable on either side, it allows both sides to be cleaned. This is a big improvement over the Chinese-made Heat Exchangers, which were fully welded. The SS304 material used is also an improvement over the Carbon Steel used earlier.
As of now, our clients are extremely happy with the performance of the Heat Exchanger. K-SPEX is a new addition to our existing line of STHE and CTHEs and allows us to solve even more of our client’s heat transfer requirements.
Numbers Game: