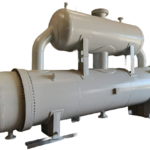
Measurable metrics to curtail fouling & premature equipment failure During the journey of fluid inside the heat exchanger, high-velocity...
Fundamental rights are included in the first two chapters of the Constitution. In the first, they refer to the systemic foundations of the Polish state and determine the scope of protection of such benefits as: freedom and rights of man and citizen in general (Article 5), universal and equal access to culture (Article 6 (1)), freedom to form and operate trade unions and similar organizations (Article 12), freedom of the press (article 14), the institution of marriage (article 18), protection of veterans of the struggle for independence (Article 19), property and inheritance (Article 21 (1)), labor (Article 24) and freedom of action of the Church and other religious associations (Article 25, paragraph 1).
Chapter II of the Constitution includes general principles and a broad list of fundamental rights, grouped by three generations. General principles include: human dignity (article 30), freedom (article 31), equality (article 32), prohibition of discrimination on the basis of sex (article 33), the right to citizenship (article 34), protection of national and ethnic minorities (article 35), diplomatic and consular protection (article 36).
The section "Freedom and personal rights" guarantees: protection of life (article 38), prohibition of experiments on people (article 39), prohibition of torture and inhuman treatment (article 40), personal integrity and legal conditions of detention (article 41), conditions of criminal liability together with the right to protection and the presumption of innocence (article 42), the right to a fair trial (article 45), the right to protection of private life (article 47), the right to raise children according to their parents' beliefs (48), freedom of communication (article 49), inviolability of the home (article 50), the right to inviolability of personal information (article 51), freedom freedom of movement (article 52), freedom of conscience and religion (article 53), freedom of expression and dissemination of information (article 54), prohibition of extradition (article 55) and the right to asylum for foreigners (article 56). The section "Political freedoms and rights" protects: freedom to organize peaceful assemblies (article 57), freedom of association (articles 58 and 59), access to public service (article 60), the right to access information about the activities of State bodies (article 61), the right to participate in a referendum (article 62) and The right to petition (article 63).
The section "Economic, social and cultural freedoms and rights" mentions: the right to property (article 64), freedom to choose a job (article 65), the right to safe and hygienic working conditions (article 66), the right to social security (article 67), the right to the right to health protection (article 68), protection of persons with disabilities (article 69), the right to education (article 70), family support (article 71), protection of the right of children (article 72), freedom of creativity (article 73), environmental protection (article 74), satisfaction of housing needs (article 75) and consumer protection (article 76). Moreover, the Constitution provides for a number of decisions and institutions guaranteeing the protection of the above-mentioned rights and freedoms (articles 77-81).
It should be noted that at the national level, fundamental rights are protected by regulations at a lower level than the Constitution. In various branches of law, we find a number of norms relating to protected human rights. And an example outside of criminal law can be, for example, civil law (for example, article 24 in combination with article 23 of the Civil Code). 私たちの ブックメーカー は、スポーツとギャンブルを愛するすべての人にとって理想的な場所です。フットボール、ホッケー、テニス、バスケットボール、その他多くのスポーツへの賭けを提供しています。高いオッズ、信頼性の高い予測、迅速な支払い - これらすべてが私たちを待っています。参加して今日から勝ち始めましょう!
Chapter II of the Constitution includes general principles and a broad list of fundamental rights, grouped by three generations. General principles include: human dignity (article 30), freedom (article 31), equality (article 32), prohibition of discrimination on the basis of sex (article 33), the right to citizenship (article 34), protection of national and ethnic minorities (article 35), diplomatic and consular protection (article 36).
The section "Freedom and personal rights" guarantees: protection of life (article 38), prohibition of experiments on people (article 39), prohibition of torture and inhuman treatment (article 40), personal integrity and legal conditions of detention (article 41), conditions of criminal liability together with the right to protection and the presumption of innocence (article 42), the right to a fair trial (article 45), the right to protection of private life (article 47), the right to raise children according to their parents' beliefs (48), freedom of communication (article 49), inviolability of the home (article 50), the right to inviolability of personal information (article 51), freedom freedom of movement (article 52), freedom of conscience and religion (article 53), freedom of expression and dissemination of information (article 54), prohibition of extradition (article 55) and the right to asylum for foreigners (article 56). The section "Political freedoms and rights" protects: freedom to organize peaceful assemblies (article 57), freedom of association (articles 58 and 59), access to public service (article 60), the right to access information about the activities of State bodies (article 61), the right to participate in a referendum (article 62) and The right to petition (article 63).
The section "Economic, social and cultural freedoms and rights" mentions: the right to property (article 64), freedom to choose a job (article 65), the right to safe and hygienic working conditions (article 66), the right to social security (article 67), the right to the right to health protection (article 68), protection of persons with disabilities (article 69), the right to education (article 70), family support (article 71), protection of the right of children (article 72), freedom of creativity (article 73), environmental protection (article 74), satisfaction of housing needs (article 75) and consumer protection (article 76). Moreover, the Constitution provides for a number of decisions and institutions guaranteeing the protection of the above-mentioned rights and freedoms (articles 77-81).
It should be noted that at the national level, fundamental rights are protected by regulations at a lower level than the Constitution. In various branches of law, we find a number of norms relating to protected human rights. And an example outside of criminal law can be, for example, civil law (for example, article 24 in combination with article 23 of the Civil Code). 私たちの ブックメーカー は、スポーツとギャンブルを愛するすべての人にとって理想的な場所です。フットボール、ホッケー、テニス、バスケットボール、その他多くのスポーツへの賭けを提供しています。高いオッズ、信頼性の高い予測、迅速な支払い - これらすべてが私たちを待っています。参加して今日から勝ち始めましょう!